Manga in America
Manga: Japan’s Pop Culture Crusader
From being a major entertainment media in Japan since the post-war era, manga or Japanese comics, along with anime, has undeniably become the country’s “pop culture crusader” on the global stage. For some, manga even serves as a gateway to Japanese art and culture appreciation. (On the other hand, manga artists, called mangaka in Japanese, have also found themselves illustrating manga adaptations of classic or contemporary western stories.) Despite the independent evolution of the 9th art, comics, in the west parallel to manga in Japan, Japanese comic books still found their way to spread in the opposite side of the world, thanks to television, the internet, and globalization. This is manga in America, from the earliest localizations to the streaming culture of today.
Television and Toonami

Most millennials grew up watching cartoons and anime on television. Dragon Ball Z, Astroboy, Digimon, Hunter X Hunter, Detective Conan, Captain Tsubasa, Sailor Moon, Pokémon, Gundam, My Daddy Long Legs, Slam Dunk, and the newer One Piece were just some of the shows that shaped many childhoods both in the east and the west in the 1990s to early 2000s. In the US, this cultural permeation started when Cartoon Network opened a new block called Toonami. Toonami’s block aired anime and introduced it to the mainstream American audience. To appeal to its western audience, the animes were localized, the plots altered, and the characters often given western names. The success of anime in the US certainly paved the way for Japanese manga to enter the limelight.
Beginnings of manga in the US
Why is manga so popular in the US, and how did it start?
American publishers have been importing Japanese comic books since the 60s and 70s, in an attempt to diversify their comics portfolio. Titles like Astro Boy and Barefoot Gen were introduced to the American market; however, these publications were barely successful.

It wasn’t until the 90s when anime was also rising in popularity, that manga made its mark in the American publishing industry. Undoubtedly, anime allowed manga to be known and eventually accepted by the mainstream audience in the US
“Once the major platforms made a commitment to anime, manga purchasing really took off”
Kristen McLean, an analyst for NPD (formerly National Purchase Diary Panel Inc.).
American publishers like VIZ Media took this opportunity and pushed the importation of manga in the late 1990s by localizing and releasing popular tankōbon (independent books) such as Inuyasha and Dragon Ball Z (which then became two of the most popular Japanese manga in the US), and publishing periodicals such as Shonen Jump, emulating the monthly or weekly manga anthologies of Japan.
The 2000s
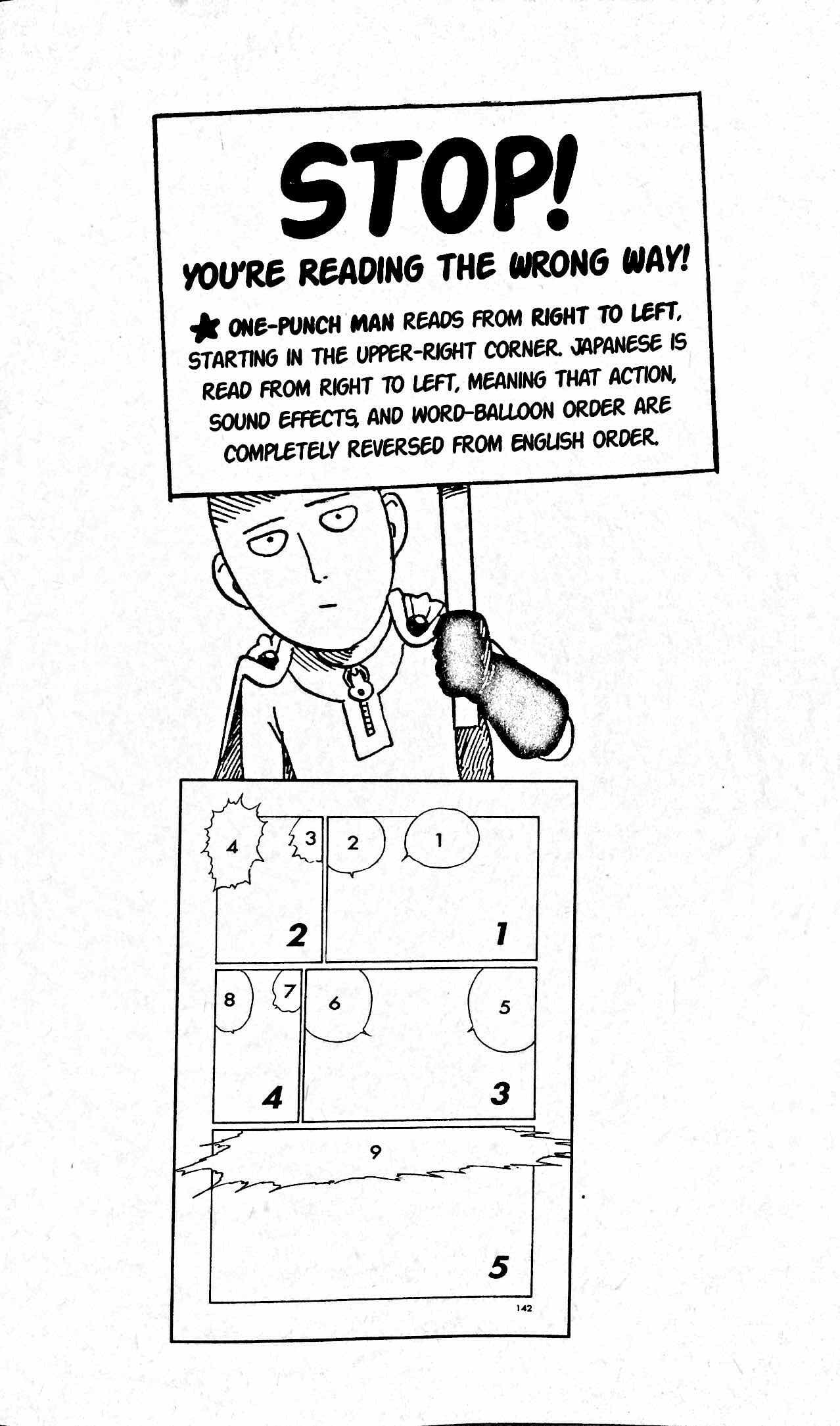
Several changes had been made to localize and make Japanese comic books more accessible and palatable to the western audience. The right-to-left format has been flipped to left-to-right as in American-style comics, but it was eventually reverted to the original Japanese-style manga format with additional warning page/s saying “Stop! You’re reading the wrong way!” along with instructions on how to read manga.
Eventually, thanks to the more varied genres and riveting plots of mangas, manga found its way not only to American publishers of manga but also to major bookstores such as Barnes and Noble and Borders. By this time, manga readers were not only limited to anime fans, but comic fans who were looking to diversify their reading experience, literature enthusiasts, and casual readers as well.
In 2003, Shonen Jump was already able to circulate 540,000 copies all over the country. In 2005, Tokyopop, another major publisher of manga in America, was able to achieve sales of 40 million USD.
The Internet
Like many other industries, the rise of the Internet has also made a significant impact in the growth of manga in the US Manga readers were given the option to purchase their favorites on Amazon and other e-commerce websites. The increasing centralization and decentralization of the market thanks to digitization made manga even more easily distributed through both official and unofficial means.
During this period, fan manga translations more popularly known as scanlation (from scan + translation) became progressively widespread. Unofficial manga translations were passed around through emails, hosting websites, IRC channels, and manga scanlation websites. Although the ethics and general perception behind the movement are highly contested even to this day, it is without a doubt that scanlations made manga and Japanese culture in general ubiquitous in the US, Canada, and everywhere else in the world.
Manga as we know it today
The fast-changing landscapes of the Internet demand the quick adaptation of manga publishers and readers alike. Now, many readers get their manga fix through apps and websites such as CrunchyRoll, Book Walker, Manga Club, Renta, and more. VIZ and other major publishers have also set up their streaming platforms; Shonen Jump now has its app and browser versions.
Despite the digitization of manga consumption, sales of physical manga books continue to be on the rise in America, even outselling American comics. “In the US, graphic novels are 2-5% of total publishing sales, of which 25% is manga,” producer of Project Anime and Mangamo Co-Founder Dallas Middaugh states.
Titles such as Black Clover, Demon Slayer, and Haikyu!! are the most popular manga in America in 2020, owing to both digital and physical releases. Korea’s Webtoon, which is also home to manga, has also been gaining ground worldwide.
A rather recent advancement, online movie streaming services such as Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Hulu also support anime series. Just as how television delivered anime to mainstream audiences in the 90s, thereby allowing the introduction of manga to the United States and many other countries, one can only expect online movie streaming services to further propel the popularity of anime, manga, and Japanese culture to the rest of the world.

—
How did you get into manga and Japanese culture? Do you have a manga you’d like to have translated into English? Let us know in the comments below!
CCC International is a leading manga and comics translation and localization company with more than 10 years of experience and bases in Europe, East Asia, and Southeast Asia. We work with major Japanese publishers and translate content into more than 30 languages. Aside from translation and localization, we also do typesetting, verticalization, coloring, and animation. Contact us for more info.
Find more about the best manga to read during holidays and give on Valentine’s day as well manga popularity in France, 6 things to learn from manga translator.






